Messer Cutting Systems has manufactured cutting-edge technology for the metalworking industry worldwide for more than 100 years. We have perfected machinery for straight and bevel plasma cutting to ensure the quality, reliability, and efficiency of your cutting process.
Our straight and bevel plasma cutting machines are designed for peak durability and quality, ensuring your business gets the most from your investment.
Following are key features of Messer Cutting Systems’ straight and bevel plasma cutters:
- Smooth surface edges.
- Precision quality cutting.
- Variety of cutting speeds and angles.
- Diverse material usage.
Plasma Cutting Process Types
Plasma cutting is a process that was originally developed for thermal cutting of materials that were unsuitable for flame cutting such as high-alloy steels and aluminum.
Messer Cutting Systems offers two kinds of plasma cutting options: straight cutting plasma and bevel cutting plasma.
STRAIGHT CUTTING PLASMA

Messer Cutting Systems’ straight-cutting plasma products cover the gamut of cutting tasks in modern metal industries. Using different thermal cutting technologies for straight cutting, our machines—MetalMaster 3.0, EdgeMax, MetalMaster Evolution, Element 400, MetalMaster Xcel, PlateMaster II, Titan III, MPC2000, MPC2000 MC, and TMC4500 DB—can be easily adapted to your requirements. Factors such as the material, thickness, cut quality, and cutting speed should be considered when making your purchase of a straight cutting plasma machine.
BEVEL CUTTING PLASMA
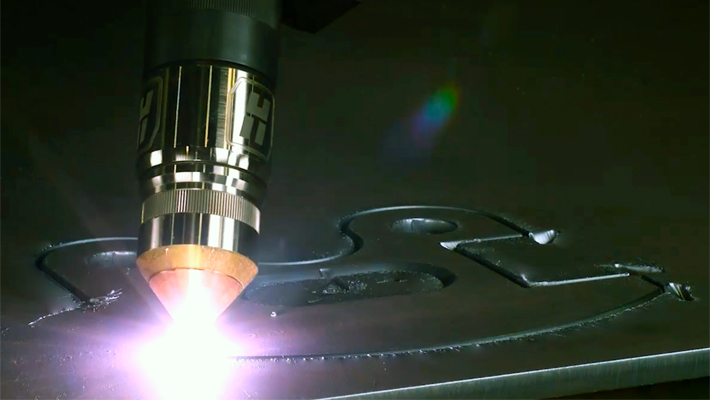

Bevel cutting requires in-depth knowledge of the machine, cutting process, and the sequential order of cutting corners, lead-ins, and lead-outs to deliver a beveled part of the highest-quality precision and accuracy. Our EdgeMax, MetalMaster Evolution, MetalMaster Xcel, PlateMaster II, Element, Titan III, MPC2000, MPC2000 MC, and TMC4500 DB bevel cutting plasma machines offer tremendous productivity and maximum robustness including many additional optional features. Just as with straight cutting plasma machines, the material, thickness, cut quality, and cutting speed should be considered when making your purchase of a bevel cutting plasma machine as well.
CUSTOM CNC PLASMA CUTTING MACHINES
Does your business require a custom CNC plasma cutter solution? Look no further.
Messer Cutting Systems provides precision custom plasma cutting machines to a number of industries, including the automotive, construction, energy, material handling, mechanical engineering, and shipbuilding industries, to name a few.
PLASMA CUTTING APPLICATIONS
Plasma cutting applications include reliably and precisely preparing metal components, including aluminum and stainless steel used in automotive repair and restoration shops, fabrication shops, industrial construction sites, and also salvage and scrapping jobs.
While exploring CNC plasma cutting tables for use in your business, some key factors to consider when making your purchase are the unit power requirements, whether you need a portable or stationary unit and the amount and thickness of metal to be cut.
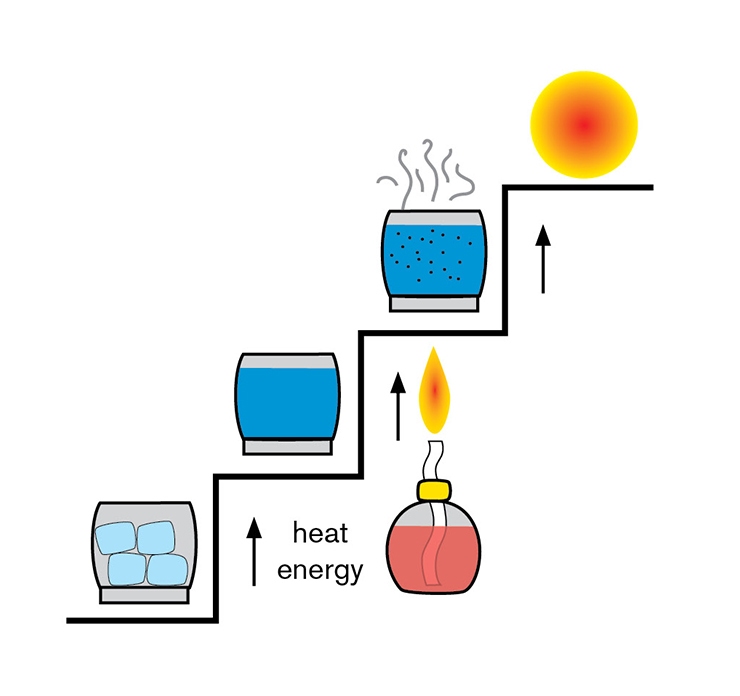
WHAT IS PLASMA? Exploring the fourth state of matter.
One common definition of plasma is to describe it as the fourth state of matter. We normally think of the three states of matter as solid, liquid, and gas.
For a common element, water, these three states are ice, water, and steam. The difference between these states relates to their energy levels. When we add energy in the form of heat to ice, the ice melts and forms water. When we add more energy into the water, it vaporizes into hydrogen and oxygen in the form of steam. By adding more energy to steam, these gases become ionized.
This ionization process causes the gas to become electrically conductive. This electrically conductive and ionized gas is called plasma.
How Does a CNC Plasma Cutter Work?
How does a CNC plasma cutter work? The plasma cutting process, as used in the cutting of electrically conductive metals, utilizes electrically conductive gas to transfer energy from an electrical power source through a plasma cutting torch to the material being cut.
Your Complete Guide to Plasma Cutting
Messer’s Guide to CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
What is CNC Plasma Cutting?
CNC plasma cutting is a precision technology used to cut metal by utilizing a high-temperature plasma arc, guided by computer numerical control (CNC) software. This method enables manufacturers and suppliers to achieve fast, accurate, and repeatable cuts on a variety of metals, making it a cornerstone in industries like construction, fabrication, and steel manufacturing.
How Does CNC Plasma Cutting Work?
At its core, CNC plasma cutting machines use a plasma torch to direct an ionized gas, such as compressed air or oxygen, at high speed onto the workpiece. High-velocity gas enters the plasma torch creating a plasma arc the plasma arc melts the molten material. The process is automated using CNC software, which controls the torch’s movement to create intricate designs or standardized cuts with various plate widths.
History and Evolution of CNC Plasma Cutting
CNC plasma cutting has evolved significantly since its inception over 60 years ago, transforming from a manual process into an advanced, automated technology that is now a staple in factories worldwide. With the integration of state-of-the-art features like multi-axis controllers and automatic torch adjustment, modern machines can handle a wide range of jobs with precision and efficiency.
From Manual to CNC: A Journey in Cutting Innovation
Initially, plasma cutting relied on manual operation, requiring skilled operators to guide the torch along cutting lines. Over time, advancements in automation introduced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems, enabling machine operators to program precise cutting paths using software like CAD/CAM solutions.
Early machines were bulky and limited in their capabilities, but brands like Messer have revolutionized the market with compact, high-performing options.
Today, automatic and desktop CNC plasma cutters are available for small workshops, while large gantry-style machines dominate industrial settings.
Key Features of Modern CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
- Automatic Controllers: Enable precise and repeatable operations, reducing manual effort and improving cut quality.
- Low Operating Costs: Machines are designed to minimize material waste, making them suitable for high-volume production lines.
- Fuel Options: Many machines combine oxygen O2 and nitrogen N2 capabilities, providing flexibility for cutting thicker materials and marking.
- Software Compatibility: Leading brands like Messer Cutting Systems supply user-friendly software programs like OmniWin to simplify programming for operators.
Whether you’re a manufacturer, supplier, or hobbyist, CNC plasma cutting machines offer unmatched versatility and efficiency. From gantry systems to portable models, the right type of CNC plasma cutter can transform your workflow, delivering high-quality results at a price point tailored to your needs.
What are the types of CNC Plasma Cutting Machines?
CNC plasma cutting systems come in various types to suit different applications:
Small Compact CNC Plasma Machines and Portable
- Plasma Cutter: Compact and cost-effective, these machines are popular among small-scale businesses and hobbyists. They offer the versatility to handle jobs on-site or in smaller workshops.
Gantry CNC Plasma Cutters: Designed for industrial applications, these heavy-duty machines operate on a gantry system, offering high precision for cutting large sheets of metal.
- Medium-Sized Table Unitized Plasma Cutters: Widely used for sheet metal fabrication, these machines are perfect for small to medium-sized operations.
- Pipe and Tube Cutting Plasma Systems: Specially designed for cutting cylindrical materials like pipes and tubes, they are an essential tool for manufacturers working with structural or decorative designs.
What are the Key Features of CNC Plasma Cutting?
- Versatility for Different Metals: CNC plasma cutting is ideal for metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and mild steel. It can cut through varying thicknesses, making it suitable for everything from thin sheets to thick structural components.
- High-Speed Precision: The process is faster than traditional flame/oxyfuel cutting and offers superior edge quality without extensive finishing work.
- Cost-Effective Operation: CNC plasma machines strike a balance between cutting speed, quality, and affordability, making them a go-to choice for manufacturers and suppliers globally.
Applications Across Industries
CNC plasma cutting machines are used extensively in:
- Factories and Manufacturing Plants: To produce components for heavy machinery or intricate designs.
- Metal Fabrication Shops: For crafting custom metal parts and decorative pieces.
- Construction: Cutting structural elements like beams and pipes.
- Art and Design: Creating detailed metal art, signage, and custom installations.
Learn more about the industries we serve at Messer.
Comparison to Other Cutting Methods
While CNC plasma cutting is a powerful solution, it’s essential to understand how it compares to other cutting methods like laser and flame cutting:
Plasma vs. Laser Cutting: Plasma is better suited for thicker materials and is more cost-effective, while laser cutting excels in ultra-fine precision.
Plasma vs. Flame Cutting: Plasma cutting is faster, more precise, and can cut a wider range of metals, whereas flame cutting is primarily used for thicker steel.
View our wide range of cutting processes, including oxyfuel cutting, laser cutting, plasma cutting, and more.
Why Choose CNC Plasma Cutting?
From crafting precision parts to fulfilling high-volume production jobs, CNC plasma cutting machines are the backbone of modern manufacturing. Whether you need a compact machine for shops with a small footprint or a robust gantry system for industrial use, the technology offers 100% customizable, scalable solutions for every factory and workshop.
Our brand features:
- High Precision: Multi-axis machines make intricate cuts possible.
- Efficiency: Automatic controllers reduce setup time and operational errors.
- Cost-Effective: Models like the MetalMaster 3.0 and Element 400 provide excellent performance at a low cost.
- Material Handling Solutions for high volume for 24-7 operations.
- Repairs and Longevity: Repair Services: Many suppliers offer support for machine repairs, spare parts, and consumables.
- Operator Training: A skilled programmer or operator can optimize parameters on the plasma power supply and machine to ensure long-term usage including light maintenance.
- Yearly Warranty: plans help with the cost of repairs.
The Various Types of CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
CNC plasma cutting machines are versatile tools designed for a variety of applications, from small workshops to large-scale industrial operations. Each type of machine offers unique features and capabilities, catering to different needs based on the materials, workspace, and level of precision required. Below is a breakdown of the most common types of CNC plasma cutting machines.
Portable CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
Portable machines are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for smaller workshops or on-site projects.
Features:
- Easy to transport and set up in different locations.
- Typically used for cutting thinner materials like mild steel or aluminum.
- Cost-effective for hobbyists or small businesses.
Applications:
- On-site metal fabrication.
- Repairs and maintenance tasks.
Advantages:
- Affordable and flexible.
- Space-saving design.
Table-type CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
These machines are designed with a fixed table where the cutting material is placed. They are common in medium to large-scale workshops.
Features:
- Comes in various sizes, such as 5’x10’, 6’ x 24’, and many more and larger configurations.
- Compatible with water tables or downdraft systems for better fume management.
- Supports cutting of thicker materials.
Applications:
- Metal fabrication for industries like construction, automotive, and manufacturing.
Advantages:
- Precision cutting with stable support for materials.
- Accommodates heavier and larger workpieces.
Pipe and Tube CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
Specialized machines designed for cylindrical workpieces such as pipes and tubes.
Features:
- Rotary attachments for rotating the material during cutting.
- Capable of cutting intersecting profiles and bevels.
Applications:
- Fabrication of pipelines, exhaust systems, and structural tubing.
Advantages:
- Tailored for precise cuts on cylindrical materials.
- Saves time compared to manual methods.
High-Definition (HD) CNC Plasma Cutting
HD plasma machines use advanced technology to achieve superior precision and edge quality.
Features:
- High-definition plasma arcs reduce dross and deliver smoother edges.
- Ideal for intricate cuts and detailed designs.
- Specialized plasma consumables for precision cutting torches.
Applications:
- Manufacturing high-precision components.
- Projects requiring minimal post-processing.
Advantages:
- Exceptional quality is suitable for demanding applications.
- Reduces material waste.
- Precision cut holes.
Combination Machines
These machines combine plasma cutting with other functions like fiber laser cutting, drilling, milling, and marking.
Features:
- Multi-functional capabilities for increased versatility.
- Saves space and reduces the need for multiple machines.
Applications:
- Sign-making, custom metal designs, and multi-step fabrication processes.
Advantages:
- Consolidates multiple processes into one machine.
- Streamlines production workflows.
The Standard and Optional Components of CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
CNC plasma cutting machines are intricate systems designed to deliver precision, efficiency, and versatility with plate cutting. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring that the machine operates smoothly and meets the demands of various cutting applications. Here’s a breakdown of the essential components and their specifications:
CNC Controller (Standard)
The CNC controller acts as the brain of the machine, interpreting cutting designs and guiding the movement of the torch.
Key Features:
- Multi-Axis Control: Enables 2D and 3D cutting for complex designs and shapes.
- Torch Height Control (THC): Automatically adjusts the torch height to maintain optimal cutting conditions, even on uneven surfaces.
- User Interface: Modern controllers often come with intuitive touchscreens and software integration for ease of use.
- Programmability: Supports various file formats like DXF and G-code, simplifying design implementation.
The Plasma Torch (Standard)
The plasma torch is responsible for generating the high-temperature plasma arc that melts and cuts through metal.
Key Features:
- Nozzle and Electrode: These are precision components that control the arc’s shape and energy. Regular replacement ensures consistent quality.
- Torch Cooling: Systems can be air- or water-cooled to prevent overheating during extended use.
- Cutting Capability: Designed for materials like steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, with thickness capabilities depending on the power supply.
- Plasma Consumable Parts: Messer stocks consumables for quick delivery.
Unitized or Gantry Style Cutting Machines (Optional)
Unitized Cutting Machines: are light / medium-duty cutting machines where the table and machine are connected, often used for fabrication and material handling operations.
Features:
- Unitized construction.
- Optional modular table sizes.
Applications:
- Material Handling operations
- Fiber laser and plasma combination cutting
Advantages:
- Low-cost and compact: machine models are offered.
- Material Construction: Made from aluminum and steel table for durability and stability.
- Drive Mechanism: Uses systems like rack-and-pinion or linear guides for smooth motion.
- Axis Movement: Supports X, Y, and in advanced models, Z-axis movement for vertical adjustments.
Gantry-style Machines: are heavy-duty systems ideal for industrial-scale operations where the table and the machine are separate.
Features:
- A gantry structure moves the torch over large cutting areas.
- Supports multi-axis cutting for complex designs.
- Available in configurations like 10 ft or more, designed for large plates.
Applications:
- Cutting large sheets of metal for structural or industrial projects.
- High-volume production lines.
Advantages:
- Exceptional durability and precision for demanding projects.
- Can handle the thickest and largest materials.
- Material Construction: Made from robust steel for durability and stability.
- Drive Mechanism: Uses systems like rack-and-pinion or linear guides for smooth motion.
- Axis Movement: Supports X, Y, and in advanced models, Z-axis movement for vertical adjustments.
Cutting Tables (Optional)
The cutting table provides the workspace for the material and ensures stability during the cutting process with manual and automatic clean-out options.
Types of Tables:
- Slagger Tables: with automatic clean-out system, with optional pit buckets.
- Water Table: A low-cost option. Water tables reduce heat distortion and capture dust and fumes, making them safer and cleaner for operators.
- Downdraft Table: Utilizes a vacuum system to extract fumes and particulates.
- Size Options: Tables come in various dimensions to accommodate different material sizes and project scopes.
Power Supply (Standard)
The power supply generates the energy needed to create the plasma arc and determines the machine’s cutting capacity.
Key Specifications:
- Output Power: Machines are rated based on their amperage of 170-800 amps to match the required material thickness and cut speed.
- Inverter Technology: Enhances efficiency and ensures consistent cutting performance.
- Voltage Compatibility: Supports single-phase or three-phase power inputs, depending on industrial or workshop needs.
Gas Supply System (Optional)
The gas supply system delivers the compressed air or other gases necessary for creating the plasma arc, choose the right gas for your operations.
- Compressed Air: Used for most cutting applications, offering affordability and efficiency.
- Oxygen and Nitrogen: Used for enhanced cutting speed or to improve edge quality.
- Argon Mixtures: Ideal for cutting stainless steel and non-ferrous metals.
- Flow Regulation: Ensures consistent pressure and delivery for smooth operation.
Drive Motors (Standard)
Drive motors move the torch and gantry across the cutting table with precision.
Types of Motors:
- Servo Motors: Found in industrial machines, offering higher precision and faster speeds.
Software (Standard)
Software bridges the gap between design and execution, converting digital files into machine-readable commands.
Optional Software offered: OmniWin, OmniBevel, and OmniFab.
Features:
- CAD/CAM Integration: Enables design creation and conversion into cutting paths.
- Nesting Algorithms: Optimizes material usage by arranging parts efficiently on the sheet.
- Simulation Tools: Allows operators to preview cuts before execution to avoid errors.
- Full automation transparency: throughout the entire workflow.
- Integrated Multi-Tool Processing: Using additional tools like drills and markers.
Optional Accessories
CNC plasma cutting machines can be customized with additional features to expand their capabilities.
- Rotary Attachments: Enable cutting of cylindrical materials like pipes and tubes.
- Bevel Cutting Heads: Allow for angled cuts, essential for weld preparation.
- Dust: Improve workplace safety by removing harmful fumes and dust generated during cutting.
- Height Sensors: Enhance precision by ensuring the torch maintains a consistent distance from the material.
- Collision Sensors and Breakaways: Prevents the torch from hitting objects on the table.
- Flex-Zones: For processing materials outside of the table.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a CNC Plasma Cutter
Selecting the right CNC plasma cutter is crucial for achieving optimal performance and efficiency in your projects. Whether you require a compact system for smaller projects or an industrial-grade machine for high-volume operations, the right combination of features ensures reliable performance and precise results. Proper maintenance and knowledge of each component will also extend the machine’s lifespan, delivering long-term value for your investment.
Below is a detailed guide to the critical considerations when choosing a CNC plasma cutter, ensuring you get the best tool for your needs.
When selecting a CNC plasma cutter, quick key specifications to evaluate include:
- Enhanced Efficiency: A well-suited machine optimizes cutting speed and reduces material waste.
- Material Type and Thickness: Ensure the machine is capable of cutting your primary materials.
- Precision Needs: Choose HD plasma machines for projects requiring high accuracy and smooth edges.
- Speed and Accuracy: Look for systems with advanced motion controls and high cutting speeds to improve productivity.
- Cutting Capacity: Match the machine’s power output to the thickness and type of materials you plan to cut.
- Budget: Balance your needs with the available budget; combination machines or second-hand options can offer good value.
- Cost Savings: The right balance of features and price ensures you get value for your investment.
- Versatility: Machines capable of handling diverse materials and tooling for secondary applications allow for expanded project possibilities.
- Scalability: High-performance machines enable businesses to scale operations as demand grows.
- Work Area Size: Match the table size to the dimensions of your typical project and fit your building footprint.
- Table Size: Ensure the cutting area fits the dimensions of your typical workpieces.
- Safety: Do you need a dust collector for smoke and dust extraction?
- Power: Do you have the proper power in your building to handle a cutting machine?
- Durability: Choose machines with high-quality components to minimize maintenance and downtime.
- Software Compatibility: Ensure the machine supports file formats and features that suit your workflow.
Choosing the right components and specifications for a CNC plasma cutting machine
Material Compatibility
The type of material you plan to cut significantly impacts your choice of CNC plasma cutter.
- Aluminum and Duct Panels: Machines designed for cutting non-ferrous metals require specific settings and consumables, such as torches with advanced gas flow controls.
- Multi-Material Capability: Ensure the machine can handle a range of materials, including mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, for diverse applications.
Machine Performance
The performance of a CNC plasma cutter is measured by its speed, precision, and cutting capacity.
- Cutting Thickness: Match the machine’s power output to the thickness of your typical workpieces.
- Speed: High-performance models are ideal for projects requiring quick turnaround, such as cutting large panels for industrial applications.
- Precision: For intricate designs like custom signs, look for machines with fine-tip torches and advanced motion controls.
Features and Accessories
Modern CNC plasma cutters come with a variety of features that enhance functionality and ease of use.
- Torch Holder: A durable and adjustable torch holder ensures stability during cutting, improving edge quality.
- Height Control: Automatic torch height control is essential for consistent cuts across uneven surfaces.
- Torch Breakaway: Protect the torch from collision.
- Software and Tutorials: Look for machines with intuitive software and access to training resources like tutorials and diagrams to simplify operations.
- Optional Equipment: that can be added to your machine.
Cost and Budget
CNC plasma cutters range from entry-level models to industrial-grade systems.
- Cheapest Options: For small-scale or hobbyist projects, affordable compact models provide basic functionality without excessive costs.
- Value for Money: Higher-end models with advanced features may have a higher initial rate but offer better long-term efficiency and reduced waste.
Applications
Your specific application will dictate the type of machine best suited to your needs.
- Duct Fabrication: Plasma cutters designed for HVAC systems are optimized for cutting precise duct panels quickly and efficiently.
- Sign Making: Machines with engraving capabilities allow for detailed custom designs.
- Industrial Use: For large-scale operations, consider machines with robust build quality and support for heavy-duty tasks.
Availability and Support
It’s essential to choose a reliable supplier or distributor for your machine.
- Exporters and Distributors: Look for reputable exporters who can provide machines with warranties and after-sales support.
- Local Depots: Having a service depot nearby ensures timely maintenance and reduces downtime.
- Vacancies in Expertise: If you lack skilled operators, consider models with user-friendly features or access to comprehensive training resources.
Maintenance and Longevity
Proper maintenance ensures that your plasma cutter delivers consistent performance over its lifetime.
- Burn Management: Regularly inspect and replace consumables like nozzles and electrodes to avoid quality degradation.
- Preventive Care: Periodic servicing reduces the risk of breakdowns, saving both time and money.
The diversity of CNC plasma cutting machines ensures there’s a model for every need, from intricate designs in small workshops to heavy-duty industrial applications. Whether you’re cutting aluminum duct panels or creating custom signage, understanding the key factors will help you make an informed decision. By understanding the strengths and applications of each type, you can select the right machine to optimize your workflow and meet your production goals.
[View Messer’s CNC Cutting Machines]
Materials Cut with CNC Plasma Machines
CNC plasma machines are versatile tools capable of cutting a wide range of materials. The type of material, its thickness, and the intended application often dictate the specific machine features and settings required. Below is an in-depth look at the materials commonly cut with CNC plasma cutters and what makes them ideal for various projects.
Mild Steel
Mild steel is one of the most common materials cut with CNC plasma machines due to its widespread use in construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries.
- Cutting Principle: The plasma arc easily melts through mild steel, creating smooth and precise cuts.
- Thickness Range: CNC plasma machines, especially those from manufacturers like Messer, can handle steel plates from thin sheets up to several inches thick, depending on the machine’s power output.
- Applications: Structural beams, brackets, and panels for industrial and architectural projects.
- Economic Value: Mild steel offers an affordable option for high-volume production.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is valued for its strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic finish.
- Specifications:
- Plasma cutters with high-definition capabilities ensure clean edges with minimal dross.
- Water tables help reduce heat distortion during cutting.
- Uses: Tanks, kitchen equipment, medical devices, and decorative items.
- Brands to Consider: Machines from Messer are top-rated for cutting stainless steel with precision.
- Pro Tip: Adjust gas settings and use proper consumables to achieve the best results.
Aluminum
Aluminum is lightweight and highly conductive, making it slightly more challenging to cut than steel but still manageable with the right plasma cutter.
- Key Features for Cutting Aluminum:
- Requires higher power output due to its thermal properties.
- Machines with engraver attachments can add decorative or functional elements to aluminum profiles.
- Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, and custom signage.
- Economic Insight: While aluminum is pricier than mild steel, plasma cutting is an economical and efficient method for complex shapes and designs.
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is a strong, durable material commonly used in heavy machinery and infrastructure projects.
- Cutting Principle: Plasma arcs can easily penetrate and cut through high-carbon content.
- Thickness Handling: Heavy-duty gantry systems like those offered by Messer can handle carbon steel plates of considerable thickness.
- Applications: Structural supports, machinery parts, and industrial tools.
Copper and Brass
Copper and brass are conductive materials often used for decorative purposes or in electrical applications.
- Challenges:
- These materials can reflect heat, making proper settings and consumables essential.
- Plasma cutters with fine-tuned controls ensure minimal material loss.
- Applications: Electrical components, plumbing fixtures, and custom art pieces.
Specialized Materials
CNC plasma machines can also handle a variety of other materials, including:
-
- Galvanized Steel: Requires precise control to avoid damaging the coating.
- Titanium: High-performance plasma cutters are needed for clean cuts.
- Hardox Steel: Known for its strength, toughness, and abrasion resistance.
- Exotic Alloys: Found in aerospace and medical industries, requiring precision and specialized settings.
Tips for Material-Specific Cutting
- Using Messer cutting machines our controls automatically adjust plasma gas settings: For materials like stainless steel or aluminum, it calibrates the appropriate gases such as oxygen or argon-hydrogen mixtures.
- Use Proper Consumables: Nozzles and electrodes from reputable manufacturers like Messer ensure consistent performance.
- Follow Tutorials and Diagrams: Access online tutorials, videos, and diagrams for material-specific guidance.
Why Material Choice Matters
From mild steel to exotic alloys, CNC plasma cutting machines are capable of handling a diverse array of materials. Understanding the specific requirements for each material helps you select the right machine, achieve high-quality results, and optimize your workflow. Whether you’re working on industrial-grade plates or intricate decorative designs, a CNC plasma cutting machine is a versatile and valuable tool for your operations.
- If budget is a concern, the lowest cost options from trusted companies near your location may suffice for simpler tasks for one-time run-offs.
- Consider machines with multi-functional capabilities, such as milling/drilling or profiling, for added versatility to offer to your customers.
Advantages of CNC Plasma Cutting
CNC plasma cutting offers numerous advantages that make it a preferred method in various industries. From its ability to handle complex designs to its cost-effectiveness, CNC plasma cutting is a game-changer for metal fabrication. Here’s a detailed look at its advantages, along with considerations of its limitations to give a balanced view.
Precision and Performance
CNC plasma machines deliver high levels of accuracy and consistency, even for intricate designs.
- Straight and Bevel Cuts: Plasma cutters excel at creating precise, cuts with smooth edges, minimizing the need for post-cut processing welding.
- Performance Benefits: Machines with professional-grade capabilities offer exceptional cutting quality, and handling materials like aluminum, and stainless steel with ease.
- Consistency: Advanced control systems ensure repeatable results, making them suitable for high-volume production lines.
Versatility in Materials and Applications
CNC plasma cutting is versatile, capable of cutting various metals and serving multiple industries.
- Material Range: Suitable for cutting metals like mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, hard ox, and as well as custom shapes.
- Applications: Widely used in construction, automotive, for fabricating structural steel components, custom parts, and decorative elements.
Cost-Effectiveness
- Money-Saving Benefits: Plasma cutting systems are more affordable than laser cutters, offering an excellent balance of precision and performance without a hefty price tag.
- Material Utilization: With advanced nesting software, CNC plasma cutters optimize material usage, reducing waste and saving money.
Flexibility and Portability
- Mobile Options: Compact and mobile CNC plasma cutters allow flexibility for on-site cutting or smaller workshops.
- Multi-Process Capability: Many machines support additional features, such as oxyfuel cutting, enabling users to handle thicker materials that plasma alone cannot cut.
Ease of Operation and Maintenance
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Most modern CNC plasma machines feature intuitive controls, making them accessible and easy to use for beginners. Training is provided.
- Maintainable Design: Regular maintenance, such as replacing consumables like nozzles and electrodes, is straightforward and ensures long-term reliability.
Customizability
- OEM Options: Many manufacturers offer OEM-grade machines that can be 100% customized to meet specific needs, from power output to various tooling.
- Retrofit Upgrades: CNC plasma cutting machines can often be upgraded with new software or attachments, enhancing their capabilities over time.
- Modular Designs: for different customizable table lengths.
Disadvantages of CNC Plasma Cutting
While CNC plasma cutting offers numerous benefits, it also comes with some limitations:
Material Limitations
Plasma cutting is unsuitable for non-conductive materials which limits its versatility compared to other methods like waterjet cutting.
Thickness Constraints
For extremely thick materials, plasma cutting may struggle to achieve clean edges, requiring oxyfuel or other laser cutting methods as a supplement.
Operational Challenges
- Learning Curve: While modern machines are user-friendly, achieving optimal results may still require training, especially for professional-grade machines.
- Heat Effects: High temperatures can warp thinner materials or leave a heat-affected zone, impacting precision in some applications.
- Speed: Very high-speed lasers are usually for thinner materials.
Key Considerations for Buyers
When looking to invest in a CNC plasma-cutting machine, consider the following:
- Budget and ROI: Assess how quickly the machine can convert investment into profits through efficient operations and reduced waste.
- Professional Needs: For high-end applications, prioritize features like multi-axis capabilities and straight-cutting performance.
- Export Options: Look for manufacturers offering machines built for export markets, ensuring global standards in quality and support.
Recent Innovations in CNC Plasma Cutting
Recent advancements have further improved the efficiency and functionality of CNC plasma-cutting machines.
- Nesting Plate: Robotic systems inspired by the precision of a honey bee streamline cutting paths for intricate designs.
- YouTube Tutorials: Comprehensive video guides on platforms like YouTube make it easier to learn about machine setup, operation, and troubleshooting.
- Motor Upgrades: Enhanced drive systems with servo or stepper motors improve accuracy and speed, boosting overall productivity.
Tools for Decision-Making
- Diagrams, Drawings, and Tutorials: Use visual aids to understand machine configurations and capabilities.
- Comparison Lists: Evaluate models based on their tools, costs, and user reviews.
- Performance Metrics: Check specifications like cutting speed, accuracy, and power to ensure they align with your needs.
Investing CNC plasma cutter can significantly impact your workflow, efficiency, and overall project quality. By considering factors like material compatibility, performance, and support options, you can choose a machine that meets your specific requirements. Whether you’re working on aluminum ducts, creating intricate signs, or managing industrial-scale operations, the right machine will maximize productivity and deliver exceptional results.
Resources for Learning and Support
- Diagrams and Tutorials: Visual aids and guides help new users understand machine components and processes.
- Images and Videos: Access online resources for step-by-step instructions and troubleshooting tips.
- Exporter Support: Many exporters and manufacturers offer detailed manuals, training sessions, and technical assistance.
CNC plasma cutting machines provide a balance of precision, versatility, and cost-effectiveness that makes them a valuable tool for industries ranging from manufacturing to art. While they come with some disadvantages, such as limitations on non-conductive materials and very thick metals, their maintainable design, adaptability, and ease of use make them an indispensable part of modern fabrication processes. Whether you’re cutting beams, fabricating custom parts, or managing large-scale projects, CNC plasma cutters deliver the performance and reliability you need to succeed.
Safety Guidelines and Risk Management for CNC Plasma Cutting
Operating CNC plasma cutting machines requires adherence to strict safety protocols to mitigate potential hazards and ensure a safe working environment. From physical risks to equipment-related challenges, understanding these factors helps operators minimize accidents and maintain productivity.
Common Hazards in CNC Plasma Cutting
CNC plasma cutting involves high temperatures, electrical systems, and compressed gases, all of which can pose risks if not handled properly.
- Fire and Heat Hazards: Plasma arcs generate extreme heat, which can ignite nearby flammable materials. Heat-affected zones on metals like stainless steel can create weak points if mishandled.
- Fume Emission: Cutting metals, especially stainless steel and galvanized materials releases toxic fumes that require proper ventilation or a dust collector extraction system.
- Electrical Risks: Improper grounding or equipment malfunctions can result in electric shocks.
- Mechanical Injuries: Moving parts such as gantries and motors pose risks if safety guards are not in place.
Risk Assessment Checklist
A thorough risk assessment ensures that potential issues are identified and mitigated before operations begin. Here’s a checklist for CNC plasma cutting safety:
Pre-Operation:
Ensure the machine is properly grounded.
Inspect consumables like nozzles and electrodes for wear.
Check gas connections for leaks.
Confirm that all safety guards are in place.
During Operation:
Wear personal protective equipment (PPE), safety glasses, and shop coats.
Monitor the cutting area for excessive heat or sparks.
Be watchful of moving parts.
Post-Operation:
Turn off the power and gas supply after cutting.
Inspect the workspace for leftover sparks or embers.
Perform routine maintenance to keep the machine in optimal condition.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
CNC plasma cutting machines can experience performance issues over time. Understanding and resolving these problems quickly is crucial to maintaining efficiency.
Cut Quality Issues:
Uneven or jagged edges can result from worn consumables or incorrect torch height.
Gas Supply Problems:
Insufficient gas pressure leads to poor arc stability.
Electrical Failures:
Power fluctuations or faulty wiring can disrupt operations.
Performance Drops:
Regular maintenance and part replacement are key to preventing performance degradation.
Training and Resources
Proper training minimizes operational risks and ensures the safe handling of CNC plasma machines. Educational materials and tools include:
PPT Presentations: Use pre-designed safety presentations to train employees on hazards and best practices.
In-house and on-site training with our Application Engineers on how to use the machine will train you on all the safety procedures.
Videos and Tutorials: Access step-by-step guides on safety protocols from platforms like YouTube.
Maintenance and Service
Routine maintenance ensures that CNC plasma cutters perform at their best while reducing the likelihood of accidents.
Scheduled Service: Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule to replace consumables and inspect the machine.
Checklist for Servicing:
- Clean the torch and cutting table regularly.
- Inspect and replace worn-out parts.
- Test the electrical systems for proper grounding and stability.
Specialized Applications and Unique Risks
Some advanced uses of CNC plasma cutting machines introduce additional safety considerations:
Underwater Cutting: Used for specific projects, this method reduces noise and fume emissions but requires advanced equipment and operator expertise. The tables must be drained to OSHA standards.
Cutting Exotic Metals: Materials like aluminum releases release dust and fumes particulates which are explosive and must be managed with high-grade dust collection ventilation systems, and spark traps.
Available Resources for Safety
Safety Tutorials: These are provided during training for risk management guidelines.
Industry Reports: Access safety ratings and machine performance reports to choose reliable products.
Operator Manuals: are included with your cutting machine.
CNC plasma cutting is a powerful and efficient process, but it comes with inherent risks that must be carefully managed. By following a thorough checklist, conducting regular risk assessments, and utilizing manuals operators can ensure safe and efficient operations. Whether you’re working with aluminum, managing underwater projects, or tackling new challenges, a proactive approach to safety will maintain both productivity and peace of mind.
With 360° Messer Service we offer you five-star service programs ensuring your machine’s productivity and longevity. View our helpful resources — from virtual service to software support — and see how we can help you with your Messer CNC plasma cutting machine.
Setting Up and Operating a CNC Plasma Cutter
Proper setup and operation of a CNC plasma cutter are crucial to achieving high-quality results and maintaining efficient workflows. Whether you are cutting aluminum panels, steel plates, or custom profiles, following a structured approach ensures safety, precision, and optimal performance. Here’s a comprehensive guide to setting up and operating your CNC plasma cutter.
1. Initial Setup
Setting up a CNC plasma cutter involves preparing the machine, workspace, and necessary resources.
- Machine Placement:
- Place the machine on a stable surface, ensuring it has enough clearance for the gantry system to move freely.
- For large operations, align the cutting table with your line of workflow to streamline material handling.
- Gas Supply Connection: Connect the gas source, such as compressed air or acetylene, securely to the machine. Ensure the gas type matches your material requirements.
- Electrical Requirements: Verify that the machine is connected to the proper power supply, typically single-phase or three-phase.
2. Software and Programming
The CNC software is where design and execution come together.
- Programming Designs:
- Use CAD/CAM software to create or import cutting profiles. Most machines accept DXF, SVG, or G-code file formats.
- For beginners, follow online tutorials or manufacturer guides to learn the basics of creating and optimizing cutting paths.
- Nesting Layouts: Arrange your designs efficiently on the plate to minimize waste. The advanced software offers automatic nesting features.
- Programmer Skills: A skilled programmer can optimize cutting paths, adjust feed rates, and improve machine performance.
3. Material Preparation
Properly preparing the material ensures cleaner cuts and fewer errors.
- Material Selection:
- Ensure the material matches the machine’s cutting capacity. For example:
- Thin aluminum sheets for lightweight applications.
- Thick steel plates for heavy-duty projects.
- Ensure the material matches the machine’s cutting capacity. For example:
- Panel Placement: Sometimes the operator will secure the material on the cutting table, ensuring it lies flat to avoid uneven cuts.
4. Calibration and Testing
Before starting the actual cut, calibrate the machine to ensure accuracy.
- Automatic Torch Alignment: The automatic torch alignment to the material’s surface, and ensures the correct height for optimal cutting.
- Trial Runs:Perform a test cut on scrap material to check the machine’s settings and make adjustments as needed.
- Safety Checklist: Verify that safety guards are in place and that the gas flow is stable.
5. Cutting Operation
Executing the cutting process involves monitoring the machine and ensuring smooth operation.
- Start the Cut: Load your design file and begin the cutting process. Messer machines and nest programs ensure it follows the intended path.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Adjust feed rates or torch height if needed during the cut to maintain edge quality.
- Post-Cut Inspection: Check the finished pieces for accuracy, clean edges, and minimal dross.
6. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance ensures the longevity and reliability of your CNC plasma cutter.
- Consumable Replacement: Inspect and replace worn-out nozzles and electrodes to maintain consistent quality.
- Routine Cleaning: Clean the cutting table, torch, and gas lines regularly.
- Troubleshooting Common Issues: If the machine fails to cut properly, refer to the user manual or diagram for guidance or contact Messer’s service department for help.
Advantages of Proper Setup and Operation
- Improved Performance: A well-maintained and calibrated machine delivers precise cuts and efficient operation.
- Material Optimization: Proper programming and nesting minimize material waste and reduce costs.
- Safety Assurance: Following safety protocols and setup guidelines prevents accidents and equipment damage.
- Scalable Productivity: A properly set up machine can handle high-volume production runs with consistent quality.
Setting up and operating a CNC plasma cutter requires attention to detail and a commitment to following best practices. From creating efficient cutting profiles to ensuring proper calibration, every step contributes to the machine’s performance and the quality of your output. Whether you’re working on aluminum panels, custom profiles, or industrial steel plates, investing time in setup and learning will maximize the advantages of your CNC plasma cutter.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with CNC Plasma Cutters
While CNC plasma cutters are highly reliable, occasional issues can arise during operation. Identifying and resolving these problems promptly is crucial to maintaining productivity, ensuring precision, and extending the machine’s lifespan. This section provides a guide to troubleshooting the most common CNC plasma cutting challenges and implementing effective solutions. If you are having issues with your machine please reach out to our Service or Applications departments to solve these issues.
1. Poor Cut Quality
Poor cut quality can manifest as uneven edges and excessive dross.
- Common Causes:
- Incorrect torch height or misaligned torch.
- Worn consumables like nozzles and electrodes.
- Insufficient gas flow or incorrect gas type.
- Solutions:
- Calibrate the torch height to match the material thickness.
- Replace worn consumables regularly to ensure a stable plasma arc.
- Verify gas pressure and type; for example, use oxygen for clean cuts on steel or argon mixtures for non-ferrous metals.
- Reach out to Messers Applications Engineer for assistance.
2. Inconsistent Arc Start
If the plasma arc fails to initiate consistently, cutting operations can be delayed or interrupted.
- Common Causes:
- Damaged torch parts, such as the electrode or nozzle.
- Loose or corroded connections in the electrical circuit.
- Issues with the pilot arc system.
- Solutions:
- Inspect and replace damaged torch parts.
- Clean or tighten all electrical connections.
- Test the pilot arc system for proper function and repair any faults.
3. Excessive Dross Formation
Dross (residue left along the edges of cuts) can be a sign of improper machine settings.
- Common Causes:
- Cutting speed too slow or too fast.
- Incorrect amperage settings.
- Torch positioned too high or too low.
- Solutions:
- Adjust the cutting speed to match the material type and thickness.
- Set the machine to the recommended amperage for the material.
- Use the torch height control system to maintain the optimal distance from the workpiece.
4. Uneven Cuts or Beveling inconsistencies
Beveled edges with inconsistent cut depths can affect the precision of finished pieces.
- Common Causes:
- Misaligned gantry or torch holder.
- Damaged or improperly calibrated height control system.
- Uneven material surface.
- Solutions:
- Align the gantry and torch holder to ensure straight cuts.
- Recalibrate the torch height control system to maintain consistent cutting depth.
- Secure the material firmly on the table to avoid movement during cutting.
5. Machine Stalls or Stops Mid-Cut
Unexpected stalls can disrupt workflow and waste materials.
- Common Causes:
- Overheating due to prolonged use or insufficient cooling.
- Software glitches or incorrect programming.
- Motor or drive system failure.
- Solutions:
- Allow the machine to cool between extended operations and check cooling systems.
- Review and correct the cutting program for errors.
- Inspect the motors and drive system for wear and replace faulty components.
6. Excessive Wear on Consumables
Consumables wearing out too quickly increases operational costs and downtime.
- Common Causes:
- Running the machine at incorrect amperage settings.
- Contaminants in the gas or air supply.
- Poor-quality consumables.
- Solutions:
- Set the machine to the recommended amperage for the consumables.
- Use clean parts.
- Purchase high-quality consumables from reliable suppliers.
7. Software and Programming Issues
Errors in programming can lead to inaccurate cuts or machine malfunctions.
- Common Causes:
- Incorrect file formats or corrupted design files.
- Nesting errors lead to material waste.
- Outdated or incompatible software
- Outdated control units.
- Solutions:
- Use compatible and correctly formatted design files like OmniWin.
- Employ nesting software to optimize material usage.
- Keep the software updated and consult the manufacturer for compatibility concerns.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance minimizes the likelihood of issues and ensures consistent machine performance.
Daily Tasks:
- Inspect the torch, consumables, and cutting table for damage or wear.
- Clean the machine and remove debris from the cutting area.
Weekly Checks:
- Test gas pressure and flow rates.
- Examine the drive system and motors for smooth operation.
Monthly Maintenance:
- Inspect electrical connections and tighten loose components.
- Recalibrate the torch height control system.
- Clean the machine regularly.
Resources for Troubleshooting
- User Manuals: Refer to the machine’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
- Online Tutorials: on Messersoft Youtube page for programming.
- Manufacturer Support: Many manufacturers and machine vendor equipment provide technical assistance and replacement parts.
- Peer Support: Join forums or communities of CNC plasma cutter operators to exchange tips and solutions.
Troubleshooting and maintaining your CNC plasma cutter is essential to ensure optimal performance and reduce downtime. By understanding common issues and applying the appropriate solutions, operators can maximize productivity and the lifespan of their equipment. Regular maintenance and access to educational resources empower users to handle challenges confidently and efficiently.
Messer offers the latest in innovations of CNC Plasma Cutting
The CNC plasma cutting industry continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology, environmental considerations, and the demand for higher efficiency and precision. These future trends are shaping how manufacturers, businesses, and hobbyists approach metal cutting, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Manufacturers are gearing up to use these approaches to save money and improve efficiencies.
1. Automation and Smart Systems
Automation is at the forefront of CNC plasma-cutting advancements, enabling greater efficiency and reduced human intervention.
- Robotic Integration:
- Robots equipped with CNC plasma torches are capable of performing complex cuts on 3D surfaces, such as pipes and beams.
- This integration enhances accuracy and speed, especially in industries like construction and automotive.
- Automatic Calibration: Smart systems can automatically calibrate torch height, gas flow, and cutting speed, minimizing errors and setup time.
- Unmanned Operations: Advanced machines with sensors and AI algorithms allow for completely automated workflows, ideal for large-scale production lines.
2. IoT Integration and Data-Driven Operations
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing how CNC plasma cutters are monitored and controlled.
- Real-Time Monitoring:
- IoT-enabled plasma cutters can track performance metrics like cutting speed, power consumption, and material usage in real-time.
- Remote monitoring allows operators to manage multiple machines from a central location.
- Predictive Maintenance: IoT systems use data analytics to predict when components like nozzles or electrodes will need replacement, reducing unexpected downtime.
- Cloud Connectivity: Design files and machine settings can be stored and accessed via the cloud, facilitating seamless collaboration between team members in different locations.
3. Eco-Friendly Innovations
As industries move towards sustainability, eco-friendly advancements in CNC plasma cutting are gaining traction.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern plasma cutters are designed to consume less power without compromising performance, reducing energy costs and environmental impact.
- Cleaner Operations: Dry dust collection systems and advanced fume extraction technologies minimize emissions and improve air quality in the workspace.
- Material Optimization: Advanced nesting software reduces material waste by maximizing the number of parts cut from each sheet.
4. Hybrid Systems
Hybrid systems that combine plasma cutting with other cutting methods are opening new possibilities for fabrication.
- Plasma-Laser Hybrids: These systems leverage the precision of laser cutting for intricate details while using plasma for thicker materials, offering a versatile solution for diverse projects.
- Plasma-Oxyfuel Combos: Combining plasma’s speed and precision with oxyfuel’s capability to cut extremely thick materials provides an all-in-one solution for heavy industries.
- Multi-Process Machines: Machines that integrate marking, drilling, milling, and plasma cutting streamline production workflows, reducing the need for multiple setups.
5. Advancements in Material Capabilities
CNC plasma cutting is expanding its range of material applications.
- Exotic Metals and Alloys: Innovations are enabling precise cuts on materials like titanium, Inconel, and other high-performance alloys.
- Underwater Cutting: New techniques for underwater plasma cutting are improving precision and reducing environmental impact, particularly in marine and offshore industries.
6. Enhanced User Experience
User-friendly advancements are making CNC plasma cutting more accessible to operators of all skill levels.
- Intuitive Interfaces: Touchscreen displays and simplified programming interfaces reduce the learning curve for new users.
- Tutorials and Support: Machines now often come with integrated tutorial modes or access to online training, making it easier to learn and operate.
- Modular Designs: Customizable and upgradeable machines allow users to adapt their systems as technology evolves.
- Virtual and Visual Services: For quick online service and repair.
The Road Ahead
As CNC plasma cutting technology advances, it will continue to provide businesses with faster, cleaner, and more versatile solutions for metal fabrication. By embracing automation, IoT integration, and sustainable practices, manufacturers can stay ahead of the curve, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
For businesses in need of industrial cutting solutions, staying informed about these trends is key to leveraging the full potential of CNC plasma cutting in the years to come.
Looking for more information on the right CNC cutting machines for your company? Contact Messer to get the industrial cutting solutions you need.
FAQS
What does a CNC plasma cutting machine do?
A CNC plasma cutting machine uses high-temperature ionized gas (plasma) to cut through electrically conductive materials. The machine melts the material using an electrical arc while simultaneously blowing away the molten metal with compressed gas, creating precise cuts controlled by computer numerical control (CNC) technology.
How to operate CNC plasma cutting machine?
Operating a CNC plasma cutter involves preparing CAD/CAM Software files like OmniWin will design cut paths, setting proper parameters like amperage and cut height, and ensuring proper material placement. The operator must monitor the cutting process while maintaining proper safety protocols and making adjustments as needed.
What are the maintenance requirements for a CNC plasma-cutting machine?
Maintenance of a CNC plasma cutting machine focuses on regular inspection and replacement of consumables, cleaning of the torch and filters, and calibration of height controls. Daily checks of consumables and weekly cleaning are essential, while quarterly maintenance includes thorough system inspection and filter replacement.
How does the cutting speed of a CNC plasma cutter compare to a laser cutter?
Plasma cutters generally cut faster than laser cutters on metal materials thicker than 1/4 inch, while lasers excel at cutting thinner materials. Plasma cutting speeds typically range from 20 to 200 inches per minute depending on material thickness and type.
What safety precautions should I take when operating a CNC plasma cutter?
Essential safety measures include wearing appropriate PPE including a face shield and flame-resistant clothing, ensuring proper ventilation, and maintaining a clean work area free of flammables. Proper electrical grounding and adherence to lockout/tagout procedures are also critical safety requirements.
Can I use a CNC plasma cutter for both metal and non-metal materials?
CNC plasma cutters are specifically designed for cutting electrically conductive materials like steel, aluminum, and copper. They cannot effectively cut non-conductive materials.
What are the common issues faced with CNC plasma cutting machines and how can they be resolved?
Common plasma cutting issues include poor cut quality, excessive dross, and arc stability problems. These can typically be resolved by adjusting cutting parameters like speed and amperage, maintaining consumables, and ensuring proper torch height control calibration.
CNC Plasma Cutter Characteristics:
- Typical: ⅛ inch (3 millimeters) up to 3 inches (75 millimeters).
- Plate thickness: 1/32 inch (0.8 millimeters) up to 6 inches (150 millimeters) with an 800 AMP plasma system with stainless steel or aluminum.
Key CNC Plasma Cutter Features:
- Low to high cut quality.
- Smooth, edge surface.
- Metallurgical perfect surfaces for welding.
- Medium heat input.
- High speed cutting.
- Hardening within the area of the HAZ.
- Wide range of material such as stainless steel, mild steel, and aluminum.

Get CNC Plasma Cutter Guidance From Messer Cutting Systems’ Sales Team
If you have questions about whether the plasma cutting process is ideal for applications in your facility, Messer Cutting Systems’ sales team can address your questions. Our team can discuss with you specific products, send sample parts, conduct live cutting and training demonstrations, and more.
Messer Cutting Systems’ unrivaled expertise and premium-quality CNC plasma cutting tables can help your business emerge or stay on top as an industry leader.
Contact
Messer Cutting Systems, Inc.





